Uncategorized
Fast-moving consumer goods
The World of Fast-Moving Consumer Goods: Trends and Insights
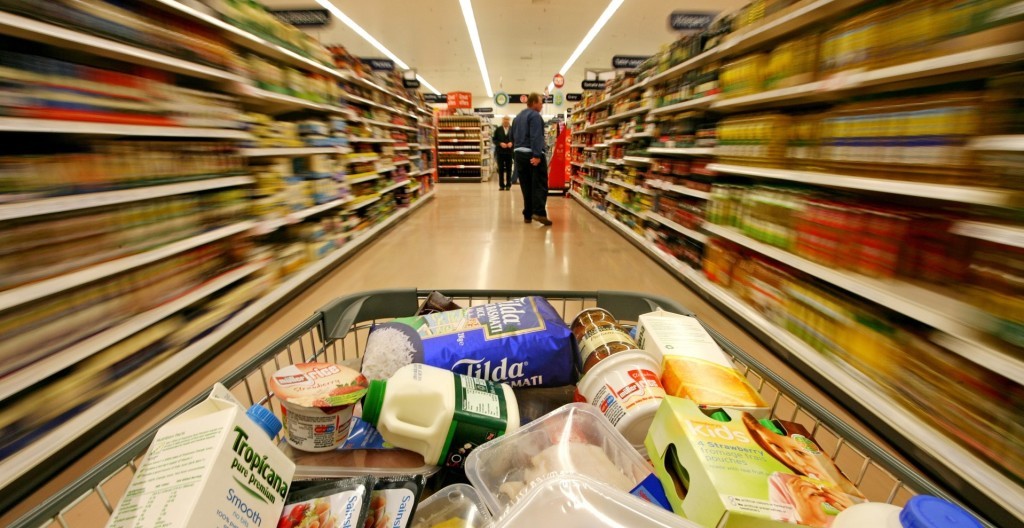
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) are the backbone of everyday life. From the toothpaste you use in the morning to the snacks you grab on the go, FMCG products are essential, highly demanded, and consumed quickly. As the industry evolves, staying ahead of emerging trends and insights is key for businesses and consumers alike.
What Defines FMCG?
FMCG refers to products that are sold quickly and at relatively low cost. These are items that are non-durable, purchased frequently, and have high turnover. Examples include food and beverages, personal care products, household items, and over-the-counter medicines.
Trends Shaping the FMCG Industry
- Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Packaging
With consumers becoming more environmentally conscious, brands are shifting toward sustainable practices. Biodegradable packaging, reduced plastic use, and carbon-neutral processes are now major selling points. - Digital Transformation
E-commerce is revolutionizing FMCG. Brands are leveraging digital platforms for direct-to-consumer sales, subscription models, and personalized marketing strategies. - Health and Wellness
A growing focus on health is influencing product innovation. Organic, plant-based, and low-sugar alternatives are gaining popularity in the food and beverage sector. - Convenience and Accessibility
Time-strapped consumers demand convenience. Ready-to-eat meals, single-serve packaging, and delivery options are becoming standard offerings. - Localization
Global brands are adopting local strategies to cater to regional tastes and preferences. This includes introducing culturally relevant flavors and products.
Challenges in the FMCG Sector
Despite its fast-paced nature, the FMCG industry faces challenges such as intense competition, fluctuating raw material costs, and the need for constant innovation. Brands must stay agile to adapt to consumer demands and market dynamics.
The Future of FMCG
As technology integrates deeper into our lives, the FMCG sector will continue evolving. Artificial intelligence, big data, and smart packaging are expected to change how products are developed, marketed, and consumed. Sustainability will remain at the forefront, with brands aiming to balance profitability with planet-friendly practices.
Understanding Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG): A Comprehensive Guide
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), also known as consumer packaged goods, are products that are sold quickly and at relatively low cost. These items are typically non-durable, meaning they have a short shelf life due to high consumer demand or perishability. Examples include food and beverages, toiletries, over-the-counter drugs, and cleaning products.
Characteristics of FMCG
- High Demand: FMCG products are essential in everyday life, making them staples in households worldwide.
- Low Cost: These goods are typically affordable, encouraging frequent purchases.
- Short Shelf Life: Many FMCG items, such as dairy products or baked goods, are perishable, while others like toiletries are consumed quickly.
- Mass Production: FMCG products are produced in large quantities to meet consumer demand efficiently.
Importance of FMCG in the Economy
FMCG companies play a critical role in the global economy. They drive employment, influence supply chains, and contribute significantly to GDP. The sector is characterized by high turnover rates, which means products are sold and replenished rapidly, ensuring steady cash flow for businesses.
Major FMCG Categories
- Food and Beverages: This includes snacks, canned goods, dairy products, and soft drinks.
- Personal Care: Skincare, haircare, oral hygiene, and cosmetics fall under this category.
- Household Products: Cleaning agents, detergents, and paper products like tissues and napkins.
- Healthcare Products: Over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and first-aid items.
Challenges in the FMCG Sector
Despite its significance, the FMCG industry faces unique challenges:
- Intense Competition: The market is saturated with brands vying for consumer attention.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Shifts toward sustainable and organic products require constant innovation.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events, such as pandemics, can impact production and distribution.
Conclusion
The FMCG industry is dynamic, fast-paced, and integral to modern life. By adapting to consumer needs and leveraging technological advancements, businesses in this sector can continue to thrive. Whether you’re a consumer or an entrepreneur, understanding FMCG is essential for navigating this ever-evolving landscape.